Our Technical Department often gets asked questions about load capacity guidelines for our Subterra products and in response to these inquiries Logix Brands has just published this technical bulletin on the subject – Halo Technical Bulletin 15 – Subterra Load Ratings.
The essence of this technical bulletin is a visual Load Chart that our technical department developed that shows the relationship between:
- The Exerted Load (Dynamic or Static)
- The Concrete Slab Thickness
- The Required Compressive Strength of the under slab Halo Subterra product.
Here is a look at our handy Load Chart:
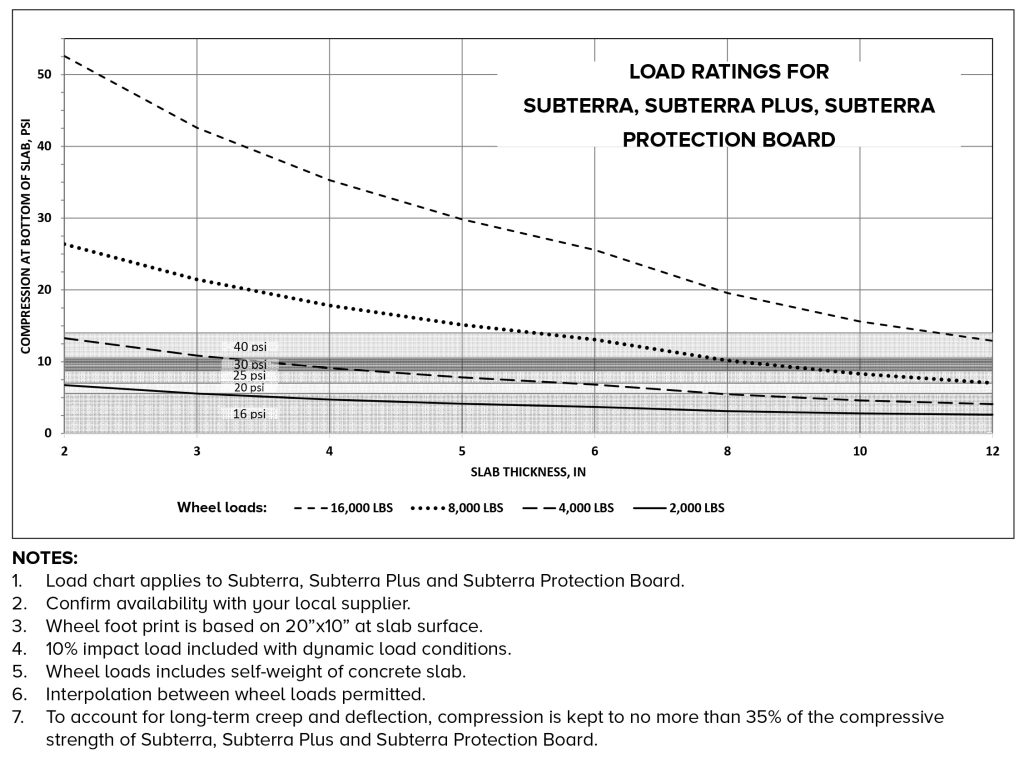
Probably the most complicated aspect of using this Load Chart is determining the load amounts being exerted. Here are a couple of tips for working out the load values:
Dynamic Loads (often referred to as Wheel Loads)
These are loads that move, like vehicles coming and going.
We typically use the calculations in the Highway Code to determine the Wheel Load value. Per the Highway Code the wheel footprint is based on a 20’ x 10” footprint. We typically also assume that 80% of a vehicles total load is transferred to the rear axel.
So, as an example, if you had a Ford 150 that weighs 8,000 lbs fully loaded, to calculate the Wheel Load exerted on the slab, allocate 80% of the weight (6,400 lbs) to the rear axel and allocated 50% to each tire (3,200 lbs per tire). In this case the exerted Wheel Load value would be 3,200 lbs.

Static Loads
These are loads that are constant and don’t move, like a heavy piece of machinery that is in place.
In this case, to calculate the amount of the load on the top of the slab, that is exerted to the slab’s bottom, you need to first calculate the load distribution area at the bottom of the slab, and then the compressive load at the bottom of the slab. It sounds complicated, but you really only have to follow these basic calculations:
Load distribution area at bottom of slab, Abot = (2t+L)(2t+W)
Compressive load at bottom of slab, w = (P/Abot)+0.0868t
In the Technical Bulletin there are 3 examples offered that show the different ways you can use this handy Load Chart. And for further assistance you can also contact us at [email protected]