Halo®’s rigid insulation system relies on an advanced graphite foam core that outperforms its leading XPS contenders in efficiency and low emissions. Halo’s products — Interra®, Exterra®, and Subterra® — are each tailored to a specific application. This post will examine the 3 different products, their intended use, and their advantages.
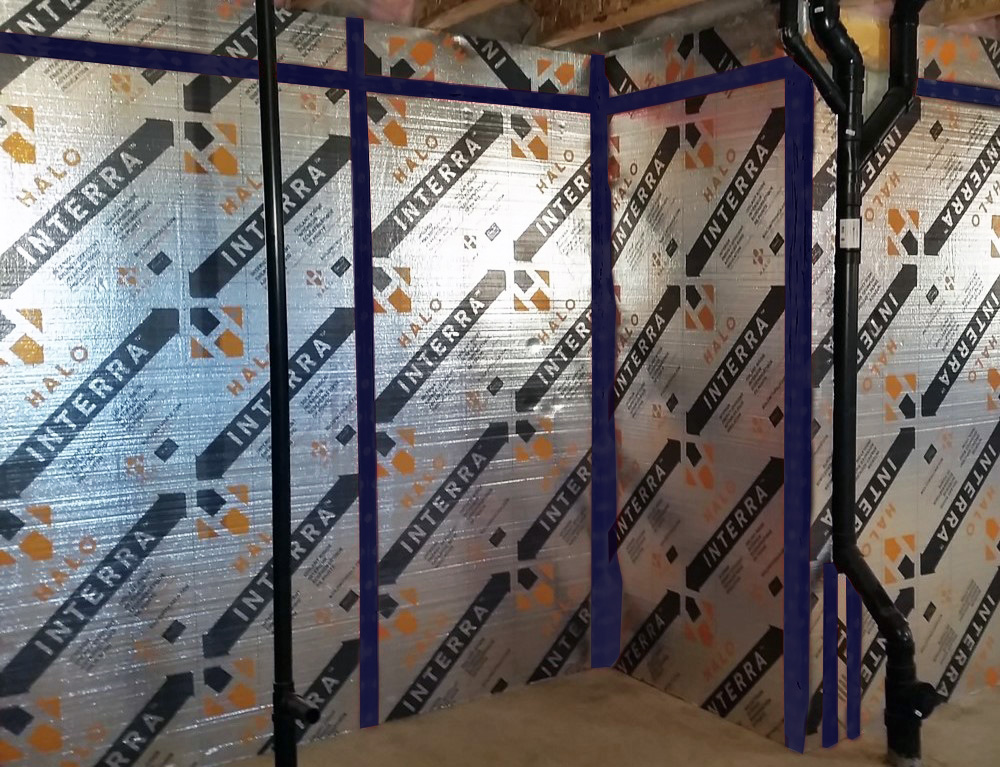
Halo®’s Interra and Interra Plus series products provide a layer of continuous insulation and an integral vapor barrier to a wall assembly’s interior side.
The Neopor GPS foam core traps the escaping heat and offers long-lasting thermal resistance of R-5/nominal inch. The boards’ laminate blocks vapor movement, so you don’t need an additional layer of poly when using Interra, providing the seams and fasteners are taped. The same laminate, which is reflective, can also reflect heat back inside the building, as long as an air gap is provided (this is easily achieved with strapping).
In residential and commercial occupancies of most US locales, Interra Plus is also a compliant thermal and ignition barrier when installed on the interior face of a wall. But using Interra Plus to insulate your basement walls, for instance, you can eliminate the need for an ignition barrier such as drywall.
Halo® Exterra is a high-performing insulation product that brings breathable, water-resistive, and energy-efficient protection to a wall assembly’s exterior face.
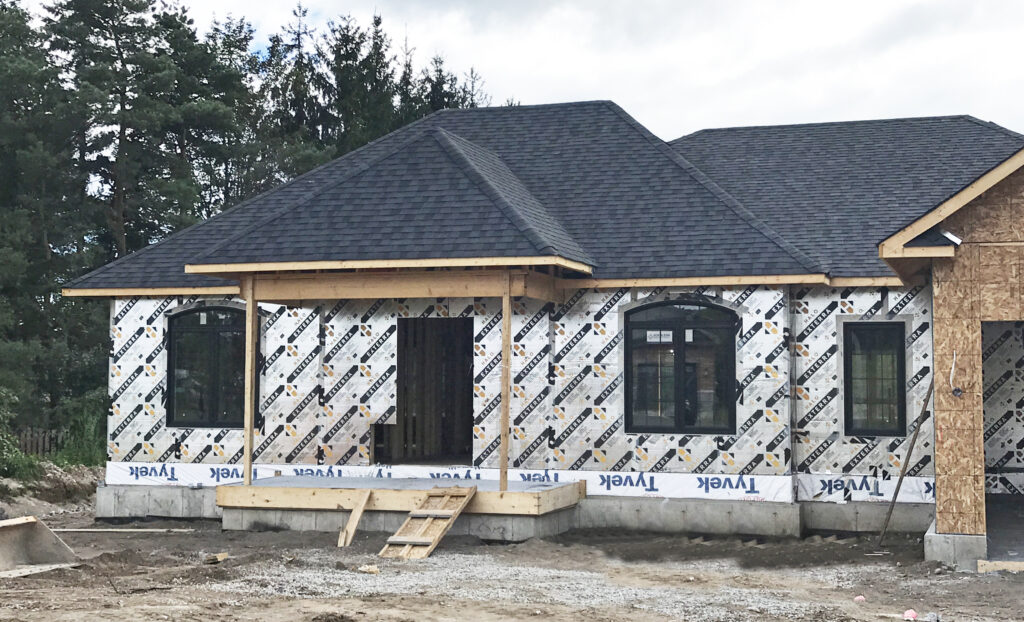


Exterra’s Neopor GPS core offers R-5 per nominal inch and creates an effective thermal break to the frame. Unlike leading XPS brands, Exterra’s R-values last longer; that’s because the GPS foam core is less prone to off-gassing and R-value deterioration over time.
The breathable nature of Exterra’s perforated laminate allows vapor to escape to the outside and keeps the wall cavity dry. That said, when the seams and fasteners are taped, Exterra’s laminate is still an effective water-resistive barrier that also blocks water from entering the wall assembly; thanks to this feature, you don’t need any additional house wrap when you build with Halo.
Halo’s Exterra easily conforms to most design configurations, including radius walls. Despite this flexibility, these laminated boards are quite durable.
Tailor-made for under-slab applications and foundation walls, Halo®’s Subterra excels below grade because of its resilient waterproof laminate.
The polypropylene film — or cross-woven laminate in Subterra Plus® — coats both sides of the GPS foam core and effectively drains water away from the concrete it protects.
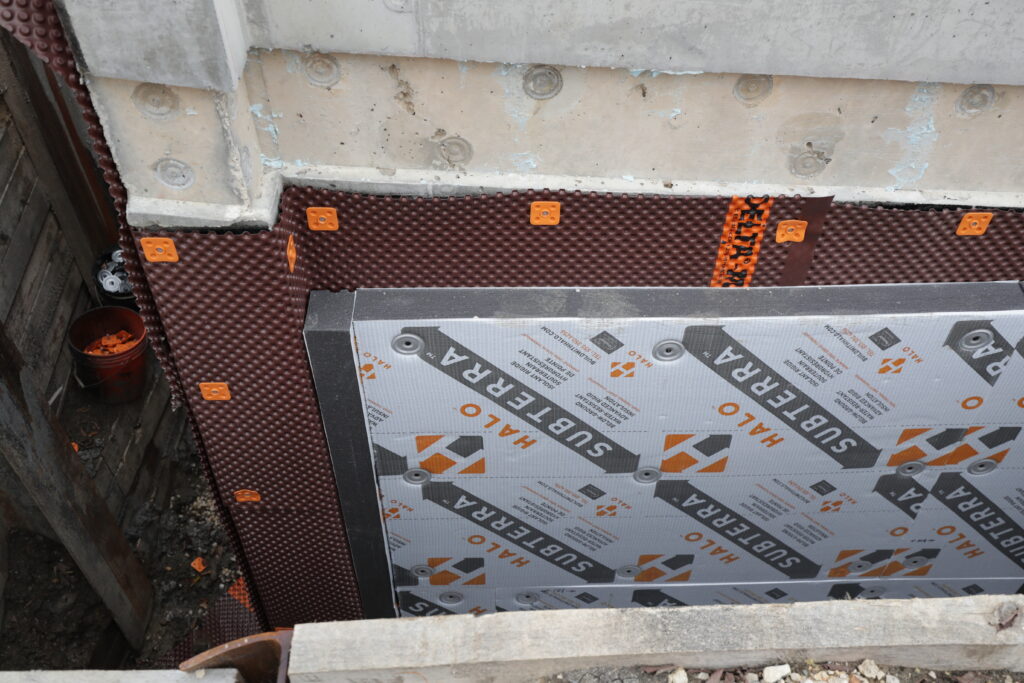


The GPS foam core, which comes in 1.0″, 1.5″, and 2.0″ standard thicknesses (custom thicknesses are also available), has a thermal resistance of R-5/nominal inch. As with all other Halo products, you can expect these R-values to last a while — GPS foam is surprisingly resistive to R-value degradation over time.
Subterra’s boards come in a variety of compressive strengths. These range from 16 PSI (110 KPA) to 30 PSI (210 KPA) — tough enough to withstand any job site traffic. However, Subterra’s strength doesn’t reduce its flexibility — both Subterra and Subterra plus easily fit all types of wall configurations, including radius walls, without the need for field cutting.

Don't miss a thing!
Subscribe for exclusive content, insider industry news and limited edition webcasts.
Wrapping it up
Halo’s Interra, Exterra, and Subterra series are each designed for a specific application. Each of the products has a unique feature that translates into a tangible benefit for the builder:
- Interra boards let you build without an additional vapor barrier and serve as a thermal/ignition barrier in the US.
- Exterra’s perforated laminate eliminates your need for house wrap while letting vapor escape the wall cavity.
- Subterra’s resilient laminate effectively diverts water away from foundation walls and protects the GPS foam core from job site damage.
All these products share one key ingredient — they’re all made with a highly efficient, low-carbon GPS foam core. Unlike XPS, GPS foam maintains its R-Values far longer, and its production releases way less CO2 into the atmosphere.