Yes, foam board insulation is flammable.
However, Neopor’s graphite polystyrene (GPS), which is used in Halo products, is treated with a fire retardant which greatly reduces flame spread and helps the fire to self-extinguish once the source of fire is removed.
Thus, Neopor, and all Halo products, are approved for the construction of homes and buildings across Canada and the USA.
In fact, thanks to its fire-resistant properties, GPS in certain low-density formulations is even allowed to be used as an interior finish without even a thermal barrier in the USA (in Canada, a thermal barrier is required).
What’s more, GPS foam board insulation is also a permitted insulation material in certain steel stud or concrete base exterior wall assemblies that are rated as non-combustible wall assemblies for use in multi-residential buildings in the USA
Status of GPS as Interior Finish In the USA — Allowed at Certain Densities and Locations
In the US, Halo’s Interra FR and Chrome GPS FR can be used in thicknesses up to 2.28 inches without a thermal or ignition barrier (such as drywall) in unfinished basements, attics, and crawl spaces.
The following test method was used by third parties to establish Neopor GPS foam boards’ lack of contribution to flame spread: NFPA 286-15, Standard Methods of Fire Tests for Evaluating Contribution of Wall and Ceiling Interior Finish to Room Fire Growth
During the third-party test, Neopor’s GPS satisfied the mandatory criteria that were set out by NFPA 286.
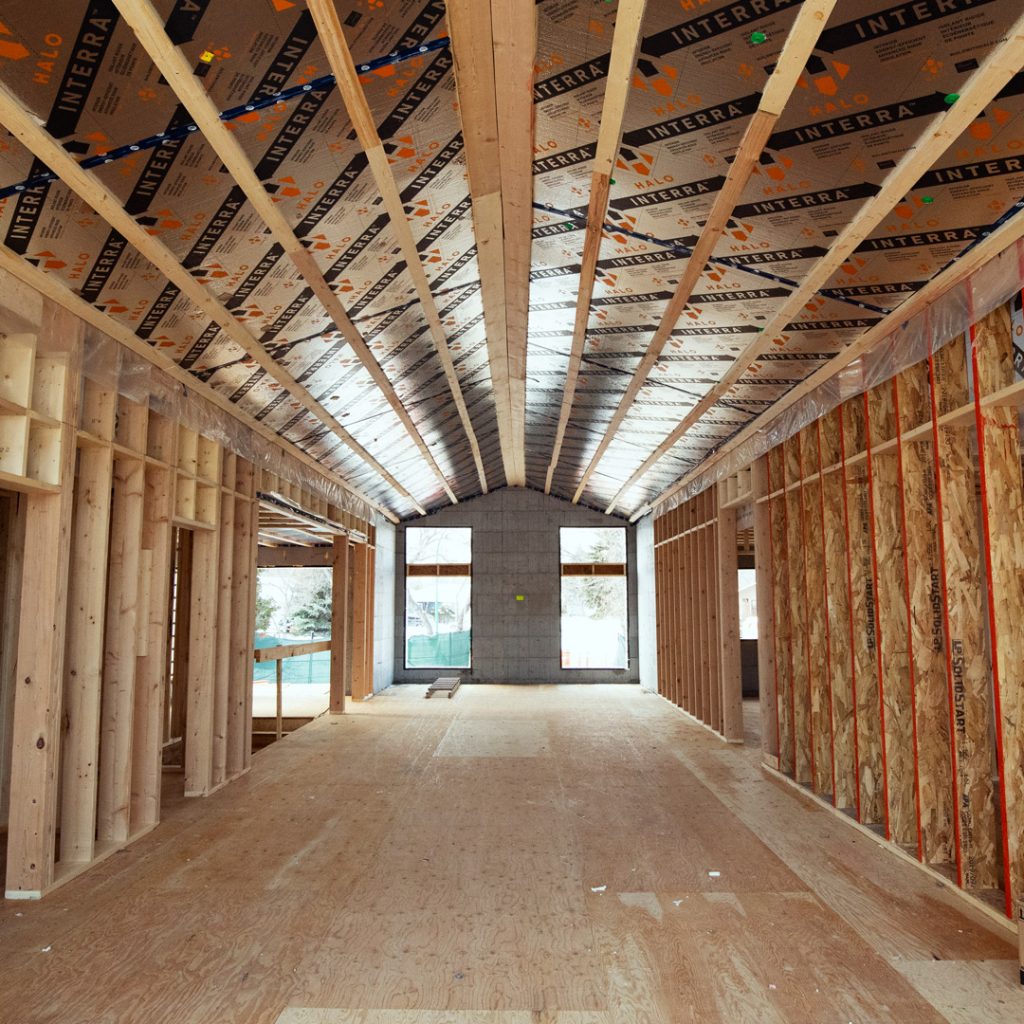

Status of GPS as an Interior Finish In Canada — Thermal Barrier Required
Despite successful testing in the US, the Canadian code still requires a thermal barrier to be used over GPS insulation products, such as Halo’s Interra of Chrome GPS.
Drywall is the accepted thermal and ignition barrier that’s generally used to protect the interior insulation.
So, if you’ve got an unfinished basement, attic, or crawl space with Halo’s Interra in Canada, installing a suitable layer of drywall is your best solution for complying with the code. The drywall layer does not have to be taped or finished.
Status of GPS In Exterior Wall Assemblies in Multi-Story Commercial and Residential Buildings
In the US, Neopor GPS foam board is an accepted insulation material in multi-story buildings of commercial and residential occupancies.
Although GPS is technically flammable, it’s passed the requisite testing that allows its use as a “combustible component” in non-combustible wall assemblies.
The test in question is the NFPA 285, which is designed to assess the flame-spread properties of exterior walls containing combustible components.
In the US, multi-story commercial and residential buildings with flammable components in their exterior wall assemblies are generally required to pass NFPA 285.
Since Neopor’s GPS foam board passed NFPA 285, it’s cleared for use in multi-story residential and commercial buildings.

Don't miss a thing!
Subscribe for exclusive content, insider industry news and limited edition webcasts.
Wrapping It Up
GPS is a flammable, yet fire-resistant rigid insulation product that can be used in certain low density formulations without an ignition barrier in the USA, and as a combustible component in exterior walls of multi-storey buildings.
Having gone through and passed NFPA 286 test, Neopor’s GPS (which is used in Halo’s insulation panels) is approved as an interior finish in the USA.
This provision applies to certain unoccupied spaces (unfinished basements, attics, crawl spaces, etc.) in residential and commercial occupancies, where Halo’s Interra and Chrome GPS can be used without an ignition barrier, such as drywall, as long as it’s not thicker than 2.28 inches.
And since Neopor’s GPS also passed NFPA 285, it’s approved for use in the exterior walls of multi-story buildings, as long as the walls have steel studs or a concrete base.